PSTN configuration¶
In this section the necessary configurations to be carried out so that our App can interact with the PSTN (public telephone network) are exposed, so that the agents can take calls from abroad as well as dial calls to external telephones.
Important
OMniLeads admite solamente SIP como tecnología de interconexión con otros conmutadores de telefonía. Por lo tanto el integrador podrá configurar troncales SIP de proveedores ITSP, troncales SIP contra sistemas PBX y/o troncales SIP contra Gateways FXO y/o E1/T1.
SIP Trunk Configuration¶
To access the trunks configuration you should click (Telephony -> SIP Trunks) and there add a new PJSIP trunk. A form similar to the one on figure will be displayed.
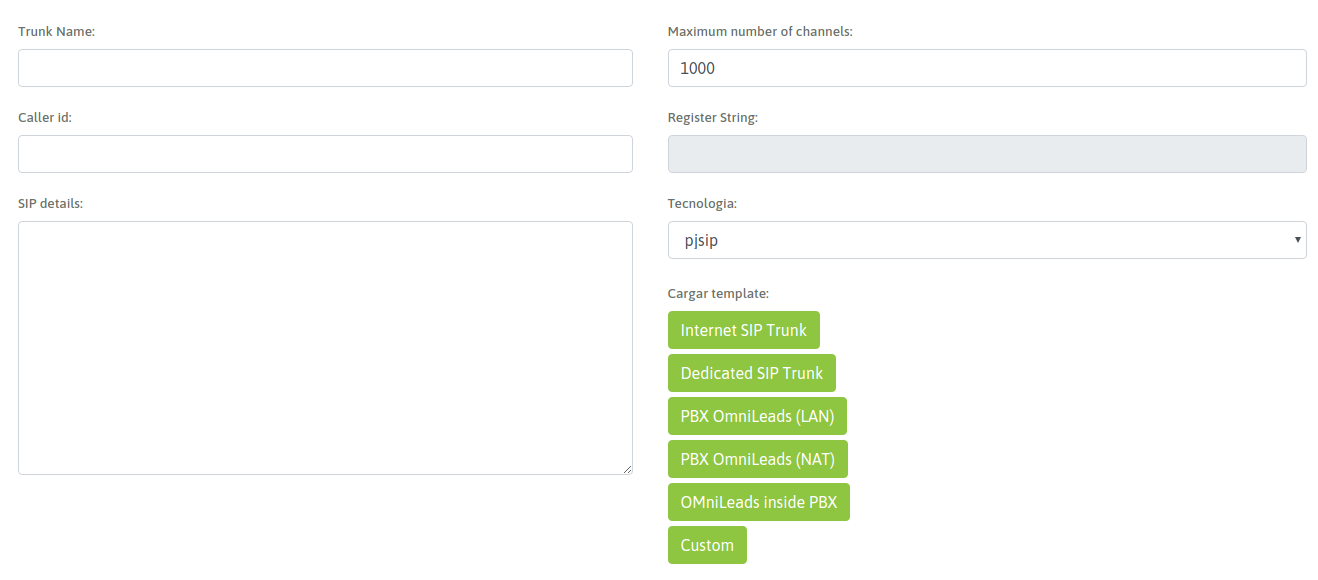
The form blanks are:
- Trunk Name: the name of the trunk. Must be alphanumeric without spaces or special characters (eg Trunk_provider_a).
- Number of channels: is the number of channels allowed by the link.
- Caller id: the number with which the calls will go through the trunk.
- SIP details: SIP parameters are provided in this text field using Asterisk PJSIP configuration Wizard syntax.
Here are some suggested templates for the types of scenarios presented as typical OMniLeads use cases.
Outbound calls routing configuration¶
OMniLeads allows to manage the outbound call routing on several SIP trunks (created previously), so using criteria like the lenght or number prefix to determine which SIP link use to route the call. It is also possible to maintain a failover logic in terms of SIP trunk.
To access the ABM of outbound routes enter the menú point (Telephony -> Outbound routes)
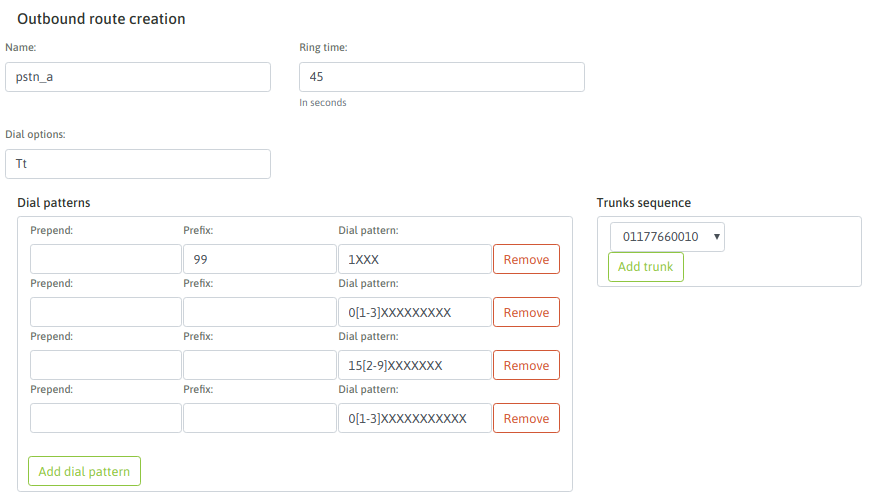
Figure 2: Outbound route
- Name: is the route name (alphanumeric without spaces)
- Ring time: is the time (in seconds) that calls made of this route, will attempt to stablish a conection with the destination, before continuing to try the next trunk or discard the call.
- Dial options: are the “dial” application options used by Asterisk(r) in a low level.
- Patrones de discado: mediante patrones, se puede representar los tipos de llamadas que serán aceptadas por la ruta y así entonces colocadas sobre el Troncal SIP para finalmente alcanzar el destino deseado.
To understand how the digits with patterns are represented, it is recommended to read this link: https://www.voip-info.org/asterisk-extension-matching/.
Within each pattern entered there are three fields:
- Prepend: are the digits sent to the SIP trunk as additionals to the dialed number. In other words, they arrive at the Trunk positioned in front of the dialed number.
- Prefix: are the digits that can come as a “prefix” of a dialed call and will be removed at the time of sending them by the SIP Trunk.
- Dial pattern: this field seeks to represent the patern of authorized digits that the route will proccess for and send to a SIP trunk to take the call out.
- Trunks sequence: are the SIP trunks on which the outbound route will attempr to stablish the dialed call by OML. If the call fails in a trunk, will attempt again in the next one.
Inbound calls routing configuration¶
The operation of incoming calls will be covered in the Incoming Campaigns section of this documentation since in order to operate with said module we should at least have created some object (IVR, time conditional, incoming campaign, etc.) to where to route each generated DID.